Everyday Relief. Everyday Protection.
Treats Sensitivity • Soothes & Moisturizes Dry Mouth Tissues
**Dose based on age

Dentin Surface Post-Treatment

Longitudinal View of Treated Dentin
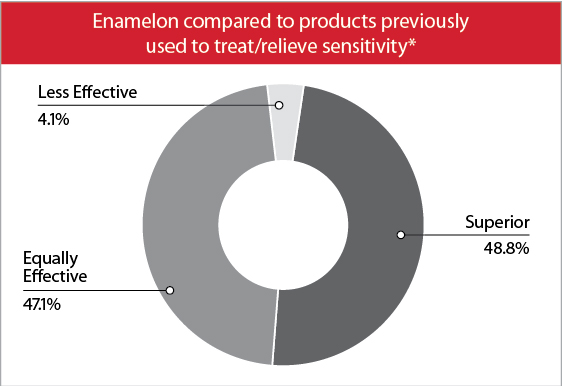
Treats sensitivity
Occludes tubules with ACP & Fluoride
Enamelon® contains stannous fluoride along with calcium and phosphate ions that have proven effective for tubule occlusion. By blocking the exposed tubules with a combination of stannous (tin) ions along with fluoride, calcium and phosphate salts, a physical barrier is created that covers open dentinal tubules to prevent external stimuli from causing pain or discomfort.
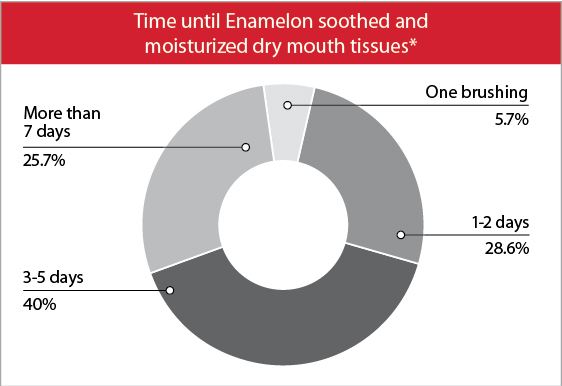
Soothes dry mouth tissue
Enamelon provides an immediate and long lasting soothing, moisturizing and lubricating effect.
Through the use of proprietary co-polymers, Ultramulsion® benefits your patients by providing a long-lasting coating that lubricates and soothes the soft tissues of the mouth.
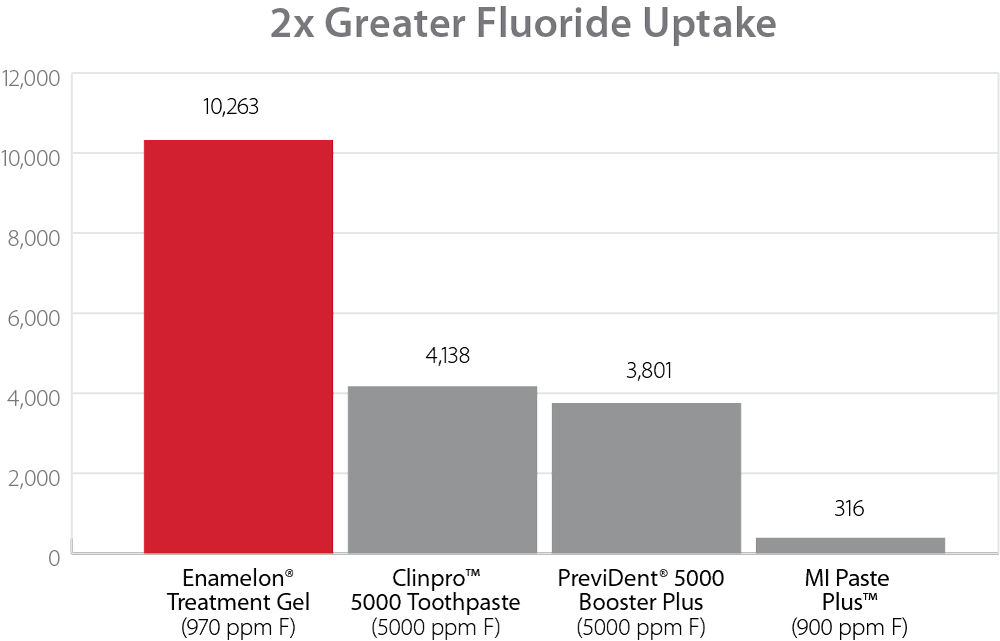
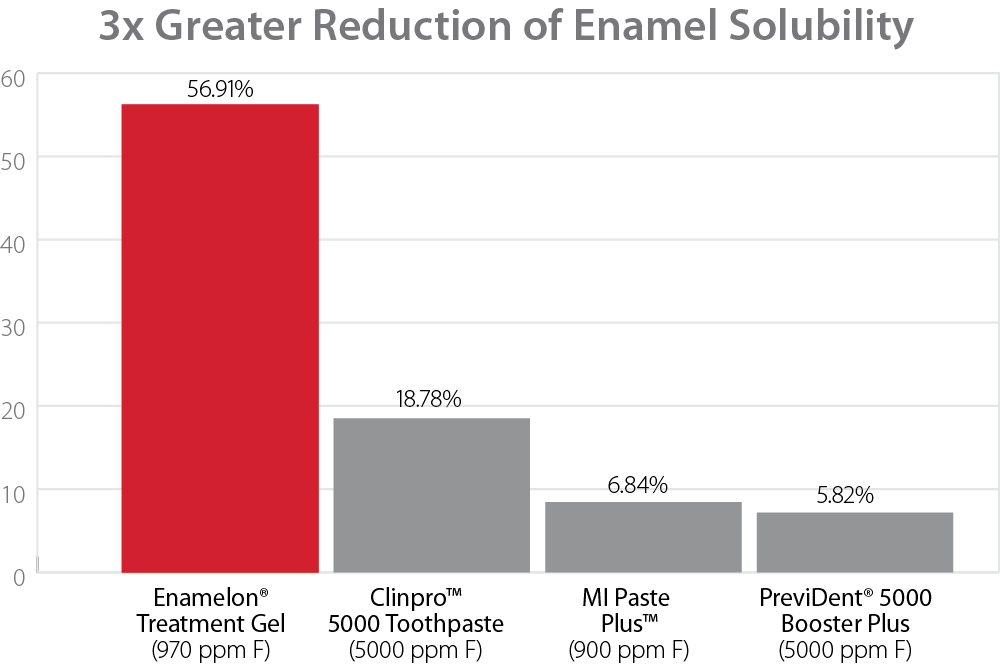
More protection, less fluoride!
*Data on file.
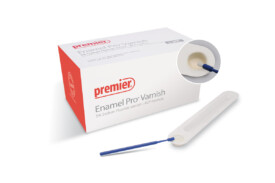
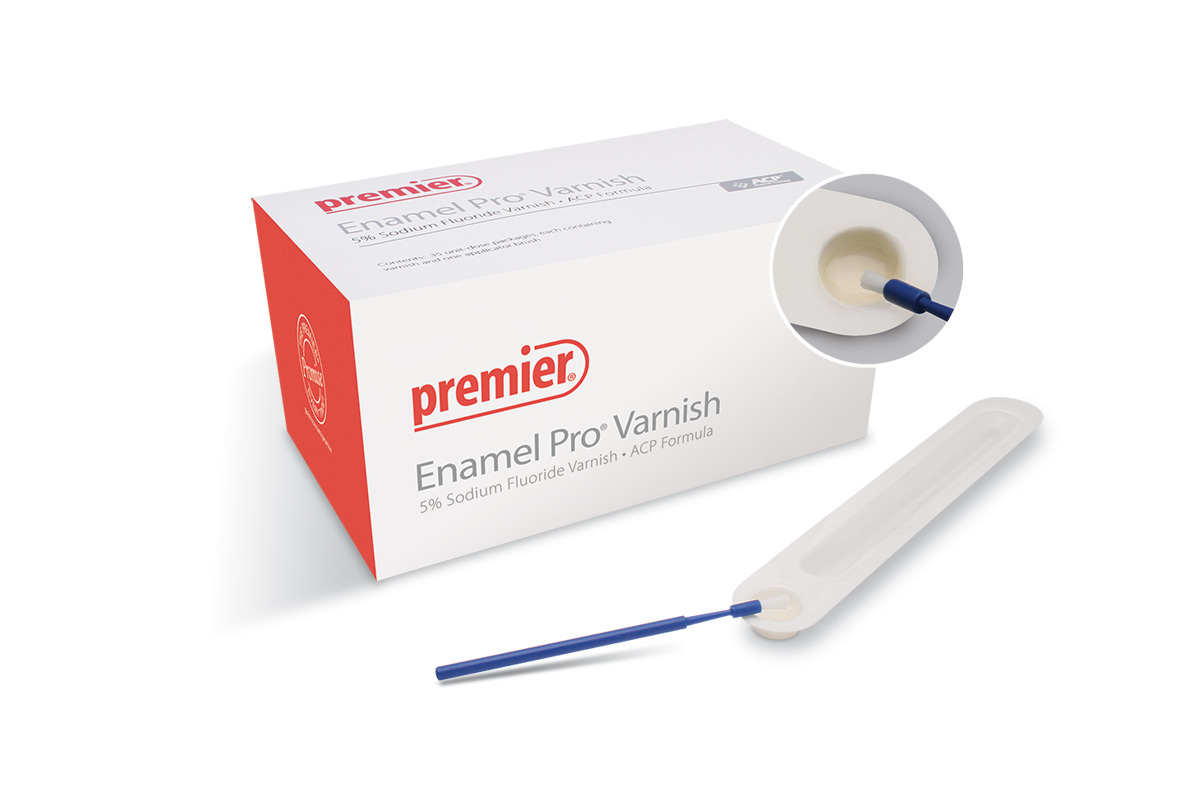
4.0 oz (113 g)
Clean Mint, 12/case
Not available in Canada.
 The most reactive and soluble calcium phosphate compound, ACP forms on the tooth enamel, within the dentinal tubules and provides a calcium and phosphate reservoir. Research shows that available ACP on the enamel can prevent damaging erosion by stimulating remineralization of tooth structure.9, 10, 11 Introducing calcium and phosphate back into the surface of the tooth with products containing ACP technology is an ideal strategy to reverse the demineralization process.
The most reactive and soluble calcium phosphate compound, ACP forms on the tooth enamel, within the dentinal tubules and provides a calcium and phosphate reservoir. Research shows that available ACP on the enamel can prevent damaging erosion by stimulating remineralization of tooth structure.9, 10, 11 Introducing calcium and phosphate back into the surface of the tooth with products containing ACP technology is an ideal strategy to reverse the demineralization process.
The ACP-forming ingredients also strengthen teeth by acting as an enhanced fluoride delivery system to deliver more fluoride than products without ACP.12 The patient has the benefit of fluoride uptake without greater exposure to higher fluoride concentrations or volumes. ACP combines with fluoride to desensitize dentin. Fluoride, along with ACP, occludes tubules by depositing tooth-like minerals to create a semi-permanent reduction in hydraulic conductance. This is a proven mechanism to reduce dentinal hypersensitivity.
Value of Fluoride Sources
Fluoride reacts with tooth mineral, forming either fluoridated apatite (firmly-bound) or calcium fluoride (loosely-bound).
Firmly-bound fluoride, incorporated onto the surface of the crystals of apatite, can reduce the solubility of tooth mineral and hence inhibit demineralization due to acids generated by plaque bacteria.13
Loosely-bound (labile F) fluoride provides a relatively slow-release form of ionic fluoride to plaque and saliva. There has been renewed interest in loosely-bound fluoride as a reaction product of fluoridation to act as a potential “reservoir” source of solution fluoride enhancing remineralization and retarding demineralization processes.14
Hydramulsion®
Hydramulsion® is composed of unique properties benefiting your patients by providing a long-lasting coating that lubricates and soothes the soft tissues of the mouth.